CO2 REMOVAL FROM HELIUM
Chemical Solvent Evaluation
LOCATION: Four Corners, AZ
MARKET: Helium Processing
THE CHALLENGE
ANUSA EPC was tasked with evaluating cost-effective methods of removing CO2 and heavy hydrocarbons from the raw helium production gas of an existing helium polishing plant. Due to unusually high concentrations of contaminants, the plant was unable to achieve its target helium purity at the facility’s nameplate capacity. Operational difficulties were forcing the plant to run below its rated capacity, leading to lost revenue.
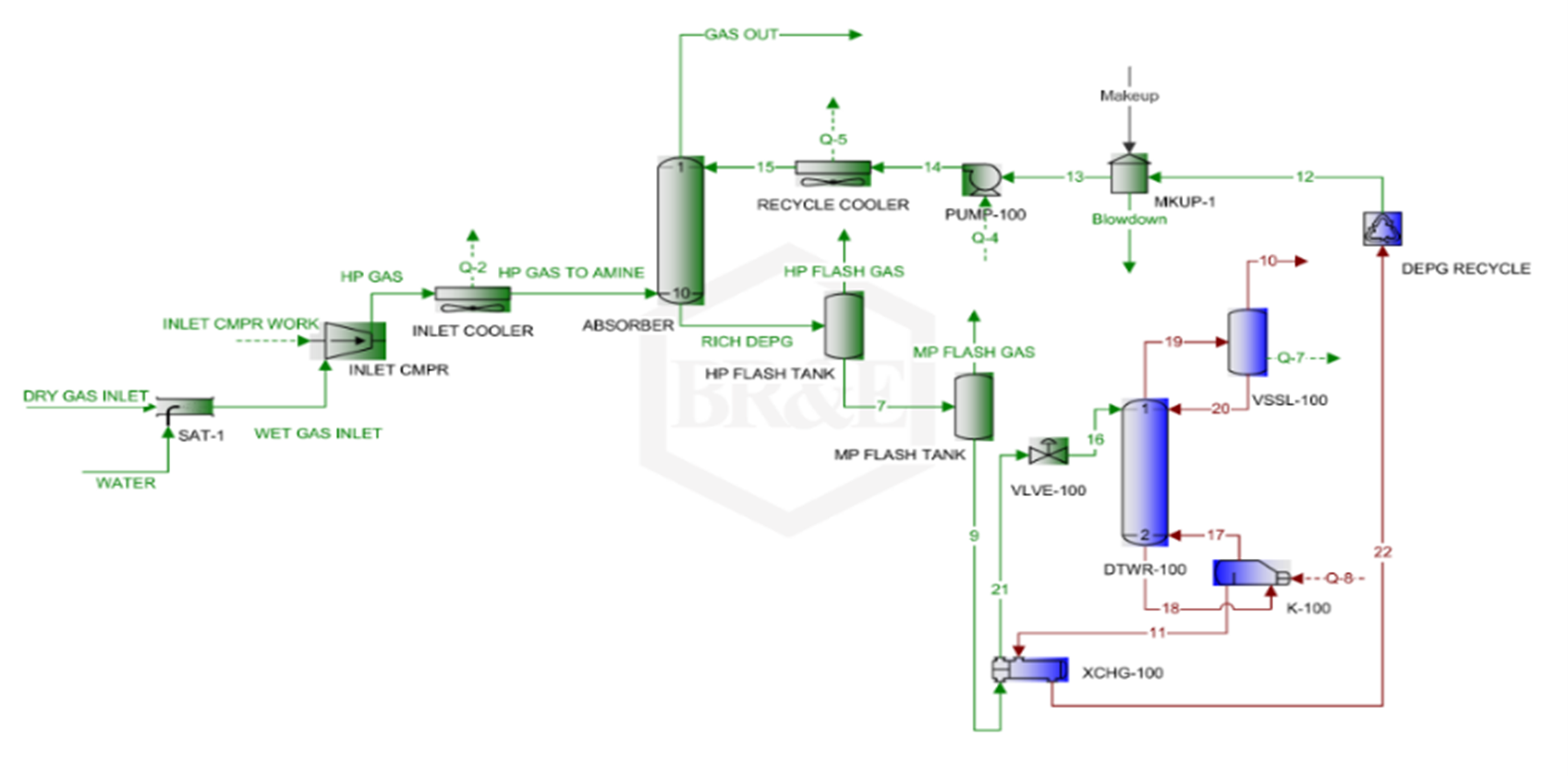
THE SOLUTION
CANUSA EPC conducted a FEED study to evaluate several different options to remove contaminants while minimizing helium losses and plant downtime.
- Process models built in ProMax based on helium gas analysis and operating conditions
- Modeled the efficiencies of chemical solvents for CO2 removal in an amine absorber
- Modeled solvent regeneration power load of all options
- Modeled inlet compression to optimize containment removal
- Chemical solvent evaluation
- Evaluated feasibility of chemical solvents, physical solvents, membranes, desiccant adsorbents, and charcoal filters for contaminant removal
- Contacted vendors for level-four cost estimates and lead times
- Evaluated OPEX changes
- Evaluated options for lowering OPEX by utilizing hydrocarbon contaminants for heat generation
- Considered opportunities to lower OPEX and increase equipment efficiency by utilizing heat exchangers
RESULT: HIGHER RATES OF RECOVERY OF HELIUM
- We provided results of advantages/disadvantages of options considered
- Included vendor data and special considerations
- Provided Class IV CAPEX and OPEX for all evaluated options
- Provided projected schedule for development
- Solution pursued by the client would reduce PSA cycles, leading to a higher rate of recovery of Helium



